Authenticated Encryption (AE) is an encryption approach that addresses confidentiality and authenticity at the same time.
Find below a summary of 4 approaches that aims to provide confidentiality and integrity at the same time.
| Approach | Description | Example of applications |
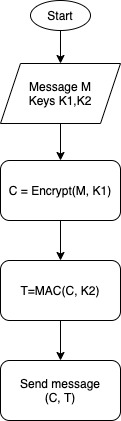
| Encrypt, then authenticate | – Generate two keys – Encrypt the message with the first key – Authenticate the encrypted message with the second key. | IPSec |
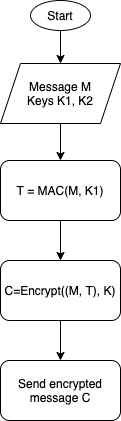
| Authenticate, then encrypt | – Generate two keys – Calculate the message authentication code using the first key – Encrypt the message plus the message authentication code using the second key | SSL and TLS |
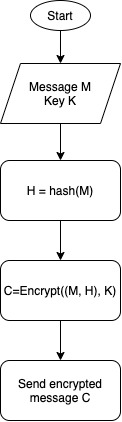
| Hash, then encrypt | – Calculate the cryptographic hash of the message. – Encrypt the message plus the hash function | Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) |
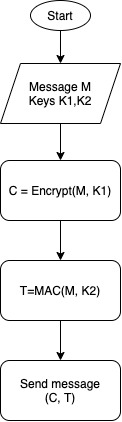
| Encrypt and authenticate | – Generate two keys – Encrypt the message with the first key – Authenticate the message (plain text) with the second key | SSH |
See below a graphic representation of each approach.
The previous approaches have some security flaws, although if used with a good design can provide a high level of security.
Fortunately for us, there are two of these designs that are NIST standards: Counter with Cipher Block Chaining-Message Authentication Code (CCM) and Galois/Counter Mode (GCM). You can get a better understanding of GCM in this link.
Related posts:
